5G is your business – even if you are in the wireline business
 5G is at the forefront of current technology discussions, promising orders of magnitude improvements in data rates, latency, number of connected devices, and overall traffic volumes when compared to today’s 4G LTE. This new generation of mobile network technology will shape and enable the evolution of augmented/virtual reality (AR/VR), IoT, esports, and Industry 4.0 applications and use cases. Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) are investing heavily in 5G, but even if you’re a regional provider of wireline services, 5G will affect your business, bringing substantial new opportunities and threats.
5G is at the forefront of current technology discussions, promising orders of magnitude improvements in data rates, latency, number of connected devices, and overall traffic volumes when compared to today’s 4G LTE. This new generation of mobile network technology will shape and enable the evolution of augmented/virtual reality (AR/VR), IoT, esports, and Industry 4.0 applications and use cases. Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) are investing heavily in 5G, but even if you’re a regional provider of wireline services, 5G will affect your business, bringing substantial new opportunities and threats.
5G will impact the entire network
5G is more than upgrading the handsets, radios, and antennas that comprise the Radio Access Network (RAN). Most of the journey content takes from the end device to the data center, where accessed content is hosted, is over (fixed) wireline networks. As 5G removes the last-mile access bottleneck, the unstoppable traffic demand of bandwidth-hungry users and applications will pulse through the entire network.
The first major impact falls over the infrastructure that connects the cell towers to the MNOs’ switching offices. It will need to deliver much higher capacity to a larger number of sites, boosting the wholesale backhaul connectivity business that relies heavily on regional infrastructure service providers.
5G New Radios (NR) will provide much faster download speeds by leveraging millimeter wave wireless spectrum - high frequency electromagnetic waves that don’t propagate far or well through buildings and obstacles - creating the need for many more small cells, much closer to subscribers, humans and machines. It means numerous new sites to interconnect, each one requiring 1Gb/s or (much) higher bandwidth, depending on the expected traffic profile. Mobile backhaul has been a key growth driver for fiber players in recent years and as it surges with 5G deployments, a new competitive environment will arise.
Another significant shift on the wireline fabric will come from the transition of radio networks to centralized/cloud-based architectures (C-RAN model). The radio intelligence, the Baseband Unit (BBU) that once sat on the base of the tower, will be moved to centralized locations and virtualized for improved cost and performance efficiencies. In 4G, these high-capacity and low-latency fronthaul connections between Radio Heads (RRHs) and BBUs were served mainly by dark fiber links, as fronthaul was closed and proprietary. Fortunately, 5G fronthaul is expected to be open and standards-based, which opens a new fronthaul services market for wholesale operators. Besides, in 5G the BBU can be split into a Centralized Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit (DU), with the connection between the two referred to as midhaul and also expected to be open and standards based. This creates a new midhaul wholesale services market for additional revenue opportunities.
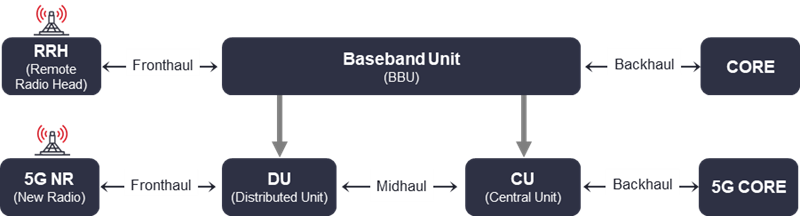
Figure 1: New C-RAN architectures
5G: Shifting the competitive landscape
Besides mobile broadband and the wholesale opportunity, 5G is expected to create a new paradigm for fixed broadband access. With 5G-powered Fixed Wireless Access (FWA), MNOs will be able to offer high-performance last-mile connectivity to support many basic business applications, which when combined with SD-WAN solutions, have the power to reshape the business services market. New service provider alternatives are likely to arise in areas where there has never been competition, and local incumbents could be threatened and need to reinvent their offerings.
One area in the spotlight: the network edge. New applications reliant on AI models and neighboring information for immediate decisions, as is the case of self-driving vehicles, will require such small latencies that processing data near the network edge - closer to the action – is a must. Distributed infrastructure may become a valued asset in this new game, and old central offices, street cabinets, and regional data centers may find new purposes in propping up the virtualized edge infrastructure that will allow these new applications to run efficiently.
5G will take IoT applications to another level, boosting the productivity of most industries. Systems, devices (sensors and actuators), and networks will be integrated with analytics and AI in industry-specific solutions tailored to solve industry-specific business challenges. This sets the stage for the rise of specialized technology integrators, positioned to lead the service relationship with enterprises. As solutions get more sophisticated, connectivity gets further commoditized, and differentiation entails a deeper understanding of customer problems.
Getting prepared for your 5G journey
Preparing to adapt is the way to thrive in a market that will be radically disrupted by 5G. All service providers, independent of their size, need a concrete plan to build adaptive capabilities and set the path to more responsive and flexible wireline networks. The combination of a Programmable Infrastructure, Analytics and Intelligence, and Software Control and Automation is the key that will enable you to excel at a game of continuously shifting rules. The Adaptive Network™ is Ciena’s blueprint to help you get there.
At Ciena, the 4G to 5G evolution is embedded in everything we do. From providing open and scalable solutions for efficient capacity growth to extending our mobile backhaul leadership to the converged 5G xHaul space, enabling smarter Adaptive IP™ architectures, to empowering the virtualized edge, Ciena is committed to helping service providers to adapt on their unique path to 5G success.
Learn how we can help you ensure success along all stages of your 5G journey.








