Three key optimization strategies to resolve state and local government network challenges
As state and local governments begin to reopen following last year’s pandemic shutdown, the importance of network connectivity is becoming paramount. One indicator of this renewed focus is that many of this year’s Digital Government Summit events include a session on “Mobility, Connectivity, and Access from Anywhere”. I have been a speaker in dozens of Digital Government Summits over the past five years, and I have rarely seen a session dedicated to network connectivity.
Wide Area Network Challenges
Even before the pandemic, government networks often struggled to support new bandwidth-intensive, latency-sensitive digital applications like artificial intelligence, video, augmented and virtual reality, analytics, and robotics. Although these applications enable government agencies to provide a higher quality citizen experience, they also strain networks. According to a survey Ciena commissioned through the Center for Digital Government, wide area networks (WANs) experience multiple challenges:
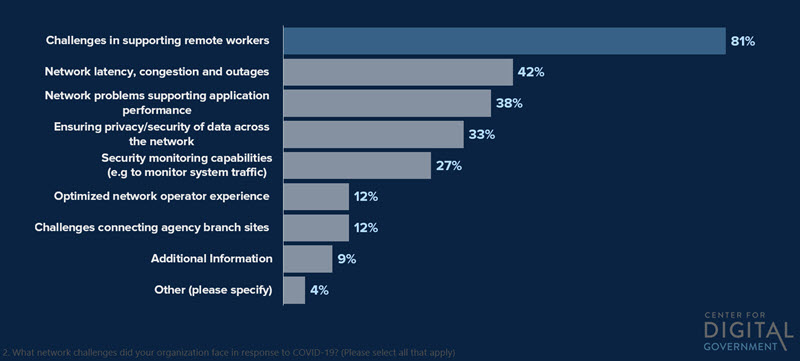
What is causing these challenges? Most state and local government WANs are a mix of legacy technologies and protocols, agency “shadow circuits”, government-owned fiber and leased connections from service providers. Network optimization can resolve these issues if done correctly.
Network Optimization
Network optimization is a set of technologies that aim to improve overall network health and performance. It is also an essential tool to provide a higher quality citizen experience, increase employee productivity, and reduce operating expenses. There are many different performance metrics that can be improved by optimizing state and local government networks. Some of the most common metrics include:
- Network availability, also known as uptime
- Bandwidth utilization and throughput
- Delay, latency, and jitter
- Packet loss
- Cost
Each state or local government situation is unique, so there is no “one size fits all” approach to network optimization. However, there are some common steps to take. One good first step is to identify the priority applications being deployed over the next couple of years that could strain the network. Ciena commissioned another study through the Center for Digital Government to identify priority applications for state and local government IT departments, highlighted in the image below.
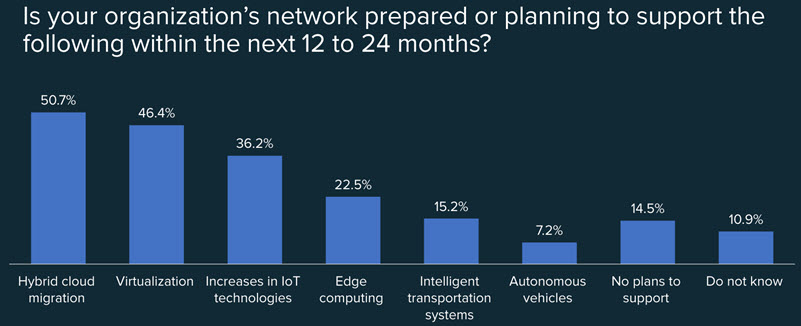
The network performance requirements of these applications drive the focus areas for network optimization. In the same survey, respondents identified key priorities in the network optimization plans to support these applications listed above. The top five priorities in order of importance were:
- Bandwidth capacity upgrades
- Network virtualization
- Network automation
- Software-Defined WAN implementation
- New network build
Recommendations for Network Optimization
For state and local government network teams, a good second step in the optimization journey is to consolidate separate agency networks and data centers into a single, converged enterprise network. This can be accomplished through deploying government-owned fiber or leasing dark fiber. For bandwidth capacity upgrades, deploying Wave Division Multiplexing (WDM) to existing fiber can optimize the fiber’s value. This fiber-optic transmission technique enables the use of multiple light wavelengths (or colors) to send data over the same medium. Two or more colors of light can travel on one fiber, and several signals can be transmitted in an optical waveguide at differing wavelengths or frequencies on the optical spectrum.
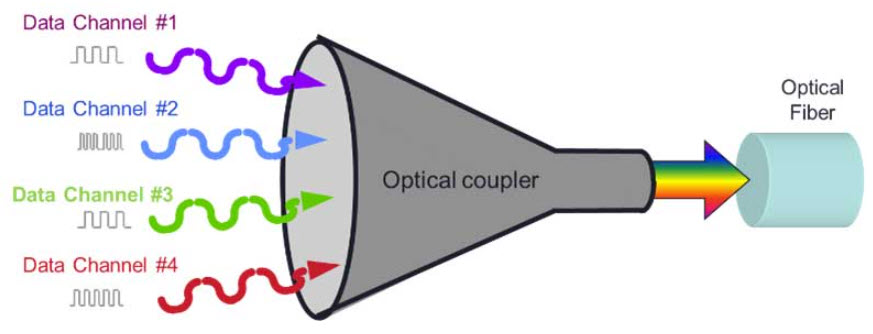
There are two types of WDM today:
- Coarse WDM (CWDM) is defined by WDM systems with fewer than eight active wavelengths per fiber. CWDM is used for short-range communications, so it employs wide-range frequencies with wavelengths that are spread far apart. CWDM is a compact and cost-effective option when spectral efficiency is not an important requirement.
- Dense WDM (DWDM) is defined in terms of frequencies. DWDM’s tighter wavelength spacing fits more channels onto a single fiber. DWDM is for systems with more than eight active wavelengths per fiber. DWDM dices spectrum finely, fitting 40-plus channels into the C-band frequency range. This enables state and local governments to maximize the performance and value of their fiber assets.
The third step in the optimization journey focuses on the agency branch locations. State and local government branches and even home-based offices can be optimized through edge virtualization. By evolving from a hardware-centric network environment to a software-based environment, state and local governments can be more agile and cost-efficient in their operations. Virtualization of the agency branch “edge” can take various forms.
- Replacing numerous network devices and application servers housed in each agency office with a single device that hosts software-based versions of the other network functions and applications
- Moving compute resources closer to agency offices and “smart” devices by hosting high-end compute servers in local micro data centers
- Providing multi-cloud integration at the branch or in the micro data center by combining high-end compute servers with a robust software stack that supports multi-tenant cloud application workloads and connectivity workloads.
Now, more than ever, state, and local governments are challenged to provide a high-quality citizen experience while operating with greater efficiency and lowering expenses. Network optimization is a critical requirement to overcome these challenges. Ciena’s network optimization solutions have helped government agencies improve employee productivity, ensure “always-on” access to digital government services, bolster disaster recovery and strengthen data security.




