Ciena has joined Google Cloud’s 5G/Edge ISV Program to help enterprises accelerate migration of their IT resources to the cloud
The shift of enterprise IT to cloud-based services continues to grow unabated and has accelerated during the pandemic. Consumption of public cloud services, such as Google Cloud, are growing collectively at a 18% CAGR according to a recent report from Omdia.
Enterprises are migrating to the cloud, not just due to lower costs, but due to greatly increased flexibility. The ability to scale up IT infrastructure during periods of peak demand and/or growth and pay for it on an on-demand basis is very attractive. An additional benefit is the ability to divide their cloud spend across one or more cloud providers and/or shift their spend from one to another is referred to as a multi-cloud model as shown in Figure 1.
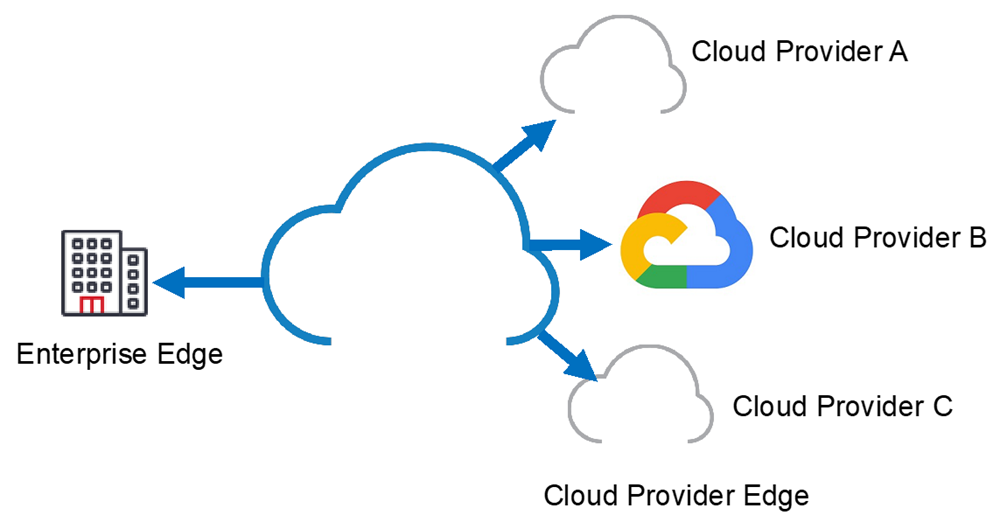
Figure 1: Enterprise to multi-cloud edge
To facilitate the migration of enterprise IT workloads to the cloud, there is a requirement for higher speed connections from the enterprise edge to cloud provider that are scalable with enhanced security to best protect critical business data. Shared IP network connections to the cloud are acceptable for lower speed (10Gb/s) connections and below. However, when secure, higher speed connections are required to the cloud, connectivity via the IP network can become overly complex, expensive, and inefficient when compared to the optical network (Optical Fast Lane) that can provide a more efficient, cost-effective, and secure option for enterprises needing to reduce their workload migration times to support their evolving business objectives.
For the multi-cloud market to succeed, it must reduce the friction for enterprises to migrate their workloads to a cloud provider, as well as between cloud providers – on demand. This is analogous to the days when you had a mobile plan with one carrier, and to switch to another carrier, you had to switch mobile numbers, which was too complex for most customers, so they stuck with their existing carrier. Only when consumers could keep their phone number when they switched carriers (through Local Number Portability), did it make the mobile market truly competitive leading to improved choice, pricing, and innovation. This is what we’re trying to achieve in the multi-cloud market.
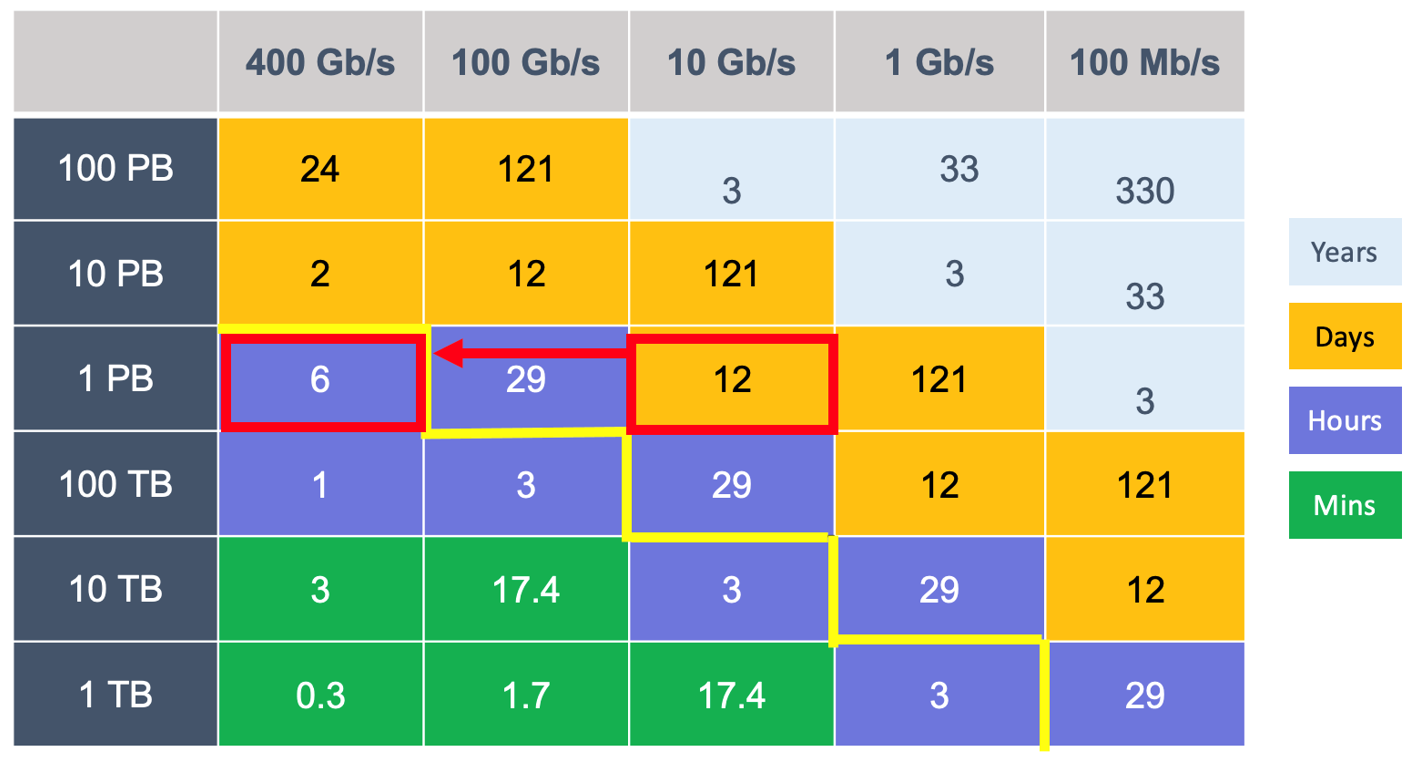
Figure 2: Cloud transfer bottlenecks for large datasets
A key area of friction for the adoption of multi-cloud services is faster workload to cloud migration times. Whether migrating data sets from an enterprise to a cloud provider or from one cloud provider to another, transferring 1 Petabyte (PB) of data at 10 Gb/s, will take 12 days as shown in Figure 2, which is unacceptable. Some cloud providers have even resorted to physical transport (e.g., 18-wheeler trucks equipped with hard drives) to address this connectivity gap.
The vision is to scale cloud connectivity so that workload migrations to the cloud would require hours instead of days. In the above example, transferring that same 1 PB at 400 Gb/s would reduce data migration time to 6 hours.
The vision of the multi-cloud market is where connectivity to the cloud is aligned with the elastic consumption model of the cloud. This is where an enterprise can request more capacity from the network to migrate a very large data set rapidly, then network capacity can be freed up for other enterprises to use.
What are the Requirements for Optical Fast Lane to Multi-Cloud?
- There is a need for direct enterprise-to-cloud connectivity that can scale from 100Gb/s to 800Gb/s on demand to reduce cloud migration times from days to hours.
- Connectivity to the cloud must be simple to request and manage, extremely reliable and secure–using tools that do not impact network performance.
What is Ciena proposing to address these market requirements?
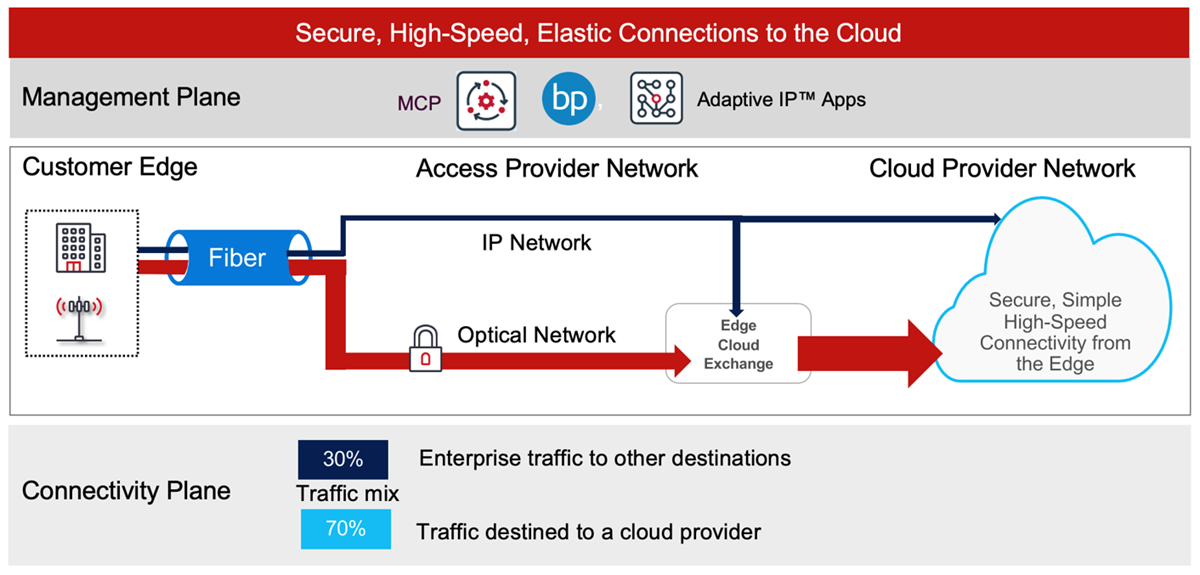
Figure 3: Secure, high-speed, Optical Fast Lane to the cloud
Ciena is proposing the architecture shown in Figure 3 that delivers an Optical Fast Lane to one of more cloud providers that meets all the requirements for a next-gen multi-cloud offering:
- Enterprise edge-to-cloud provider connectivity that can scale from 100 Gb/s to 800 Gb/s on demand to reduce cloud migration times from days to just hours, or less.
- Leverages 400ZR coherent optics to provide increased capacity over existing fiber plants. Ciena offers WaveLogic 5 Nano supporting 100 Gb/s to 400G b/s capacities in a compact form-factor that meets industry standards and supports reaches from 80 km to 120 km. This enables cloud connections up to 400 GbE that can be plugged into Ciena’s extensive portfolio of routers and switches.
- Secure connectivity with low overheard and latency via 100/400/800 Gb/s in-flight encryption.
- Multi-cloud access via a customer portal through Blue Planet Multi-Domain Service Orchestration (MDSO) automation software.
This innovative approach delivers very high-speed scalable, elastic, simple, secure connectivity to the cloud at the point where an IP-only architecture begins to hit limitations:
- IP-only can be costly and complex to scale beyond 10 Gb/s resulting in unacceptable cloud migration intervals, resulting in days vs hours.
- IP-only cannot deliver secure connectivity to the cloud without an associated bandwidth tax, increased latency and complexity of securing connectivity at the IP layer.
How are Ciena and Google Cloud embracing this approach?
Google Cloud is one of the leading cloud providers in the market that embraces an architecture that enables their enterprise customers to gracefully migrate their workloads to Google Cloud via an Optical Fast Lane that enables Enterprise to develop and leverage the Google Cloud for new and innovative applications. Ciena is excited to be a key player in this program and in addressing this opportunity in the industry. This builds off Ciena’s long standing relationship with Google and other Cloud Providers serving both private and managed high-capacity optical transport networks – principally dominated by subsea, long-haul, metro and DCI connectivity.
Ciena is also a major supplier to Communication Service Providers (CSPs) and MSOs – serving all segments of the network – including high-speed access connectivity for Enterprises as well as cell-site routing and backhaul. In partnership with CSPs, Google Cloud is helping customers leverage their edge real-estate assets to facilitate low latency connectivity to Google Cloud and reduce the friction required for enterprises to improve their mean time to the cloud for their data and workloads.
“Enterprises are increasingly migrating critical workloads and applications into the cloud, and businesses with presences at the network edge require low-latency, secure access to these applications and data. We’re excited to partner with Ciena to deliver its Adaptive Network automation software on Google Cloud, helping enable secure and fast connectivity to Google Cloud for these customers.”- Tanuj Raja, Global Head, Strategic Partnerships at Google Cloud