5G and Edge Cloud: joining forces to fuel next-generation applications
5G will account for 78% of the $1.1T mobile operators will invest in the next 5 years – that’s over $850 Billion, according to GSMA Intelligence, Mobile Economy 2021, June 2021. To sustain this capital flow and make their 5G business cases profitable, operators will need to minimize costs, increase efficiency, and develop new revenue streams. Driven by these objectives, service providers are embarking on a network evolution journey, which will both enable and leverage the emerging Edge Cloud.
What is Edge Cloud?
The Edge Cloud is a cloud ecosystem encompassing storage and compute assets located at the edge – close to the applications and users - and interconnected by a scalable, application-aware network that can sense and adapt to changing needs securely and in real-time. It focuses on providing a quick and efficient computing response for latency-sensitive or data-intensive applications. It leverages a cloud-based architecture, software-defined, with open APIs and virtualized components, which can sit either on enterprise premises, in the far edge (cell-sites, COs, local hubs), or the near edge (regional data centers). The Edge Cloud serves multiple categories of use cases and applications, with various levels of maturity:
- It is a well-established reality for streaming, where CDNs (content delivery networks) push popular or trending content to the edge, to maximize performance and optimize costs.
- Its greatest promise is the enablement of the next generation of enterprise applications that will rely on its low latency and high reliability to automate decisions in machine time.
- It is quickly growing in the telco cloud domain, with operators leveraging distributed computing resources to virtualize network functions.
Where 5G and Edge Cloud meet
Architecture innovations enabled by Edge Cloud will be critical for mobile network operators (MNOs) to cost-effectively build and evolve their 5G networks. 5G deployments will harness new spectrum, with new radios and more dense cell sites to deliver the necessary coverage and performance. The centralization and virtualization of the RAN (Radio Area Network) intelligence will be instrumental in making cell densification cheaper and more agile. It facilitates cell coordination, optimizes space and power, and minimizes truck rolls and management costs.
The efficiency gains of the cloud-RAN are supported by the telco cloud, a computing infrastructure at regional aggregation sites close to the cell sites - the C-RAN hubs. They host software performing part of the radio functions for multiple cells - the virtual Distributed Units (vDUs) and virtual Centralized Units (vCUs), which allows for simpler and cheaper Radio Units (RUs). A 5G radio system employs advanced algorithms that require strict synchronization, hence RAN centralization is only possible because the computing is performed at the edge, in a nearby site (typically, DUs are within 20Km of RUs) connected by high-capacity and low-latency fronthaul links delivering latencies below a few hundred microseconds.
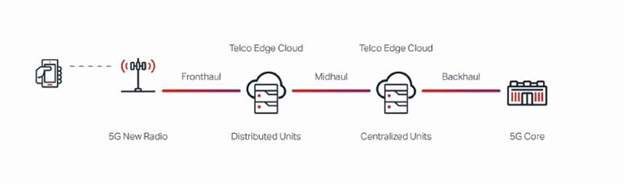
The cloud RAN is the most prominent use case of the telco cloud (which is, in turn, a subset of the Edge Cloud), but not the only one. Virtualized Edge Services leverage distributed computing elements (often on-prem) to deliver virtual network functions cost-efficiently and flexibly to enterprises. These range from basic SD-WAN to virtual routers, firewalls, WAN accelerators, and the most diverse enterprise network applications that demand the low latency only the edge can provide.
5G not only benefits from the Edge Cloud, taking advantage of it to support C-RAN architectures that minimize investments and maximize performance. It is also a catalyst of it. 5G is becoming the communication fabric connecting new sensors, wearables, drones, intelligent vehicles, and devices to AI and advanced algorithms, enabling a profound digital transformation of the most diverse industry verticals.
5G’s secure framework, mobility, high throughput, and low latency position the technology as the best suited to enable the next generation of enterprise automation. Many of these applications will also require edge computing to function properly. Some involve swift machine decisions, as when robots and automated vehicles interact in synchrony, demanding ultra-low latency and complete reliability. Others will generate enormous amounts of data from sensors that must be processed and filtered at the edge to minimize cloud or bandwidth costs.
A few may have information privacy or control issues that will require the data not to leave the premises. Therefore, in most scenarios, private 5G deployments will be coupled with Edge Cloud implementations, accelerating the edge demand as it blends connectivity and computing capabilities to address the automation of the most sensitive business processes. These premium use cases arise as valuable new revenue drivers allowing MNOs to monetize their 5G investments, further fueling its growth.
The impact of new edge applications
The new generation of edge applications is intrinsically convergent and favors the emergence of new business models. It is an ecosystem play, where mobile and wireline network operators, cloud providers, neutral hosts, datacenter providers, system integrators, and vendors will collaborate to integrate complex components into seamless solutions for customers in the most diverse fields.
Ciena has been actively working with this ecosystem to help build the next generation of metro and edge networks and applications. We simplify 5G evolution and Edge Cloud deployments, helping service providers take an Adaptive NetworkTM approach and own the edge. Ciena’s xHaul routers allow operators to cost-effectively deploy new 5G radios in multi-architecture scenarios, future-proofing their investments as they evolve through different levels of centralization, virtualization, and openness – fully leveraging the telco cloud and enabling new edge applications. With full support of soft and hard network slicing and comprehensive automation and professional services, Ciena’s 5G solutions position service providers to offer tiered SLA-based services to their customers, monetizing their networks and unlocking new revenue streams.
These are exciting times to be in the technology industry. Innovation has never been so intense, well-funded, fast, and disruptive. 5G and the Edge Cloud are melding to power innovations that can boost industries’ productivity, improve healthcare, reduce accidents, and extend access to goods, services, and information, positively transforming societies. Technology service providers of all types are instruments of these transformations. They have a singular opportunity to make the most of their infrastructure assets, expertise, network, and capabilities to thrive through it. Ciena is committed to working with them to make it happen.








