Universal aggregation for wholesale network operators
With the promise of 5G mobile networks to cover more people and places than ever before with unprecedented service performance, while 4G LTE keeps customers connected, Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and wholesaler’s business is booming with what seems like a new Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) launching each week. To fend off competitive threats, most MNO/MNVOs make use of newly formed Mobile Virtual Network Enablers (MVNEs) and Mobile Network Virtual Aggregators (MNVAs) to forge partnerships as even the traditional wholesaler cannot keep up.
As operators continue to evolve their networks to 5G there are a number of potential risks if operators don’t address infrastructure sprawl, scale, and complexity. Their goal is to increase service speeds by investing heavily in their access networks to accommodate future service growth and ensure their advertised speeds and services surpass the competition. To do so they will need an architecture that leverages universal aggregation.
What is Universal Aggregation?
Universal aggregation provides increased choice and control of tangible business value assets like coherent optics, pluggable dedicated and shared fiber, and Adaptive IPTM. This choice is enabled by platforms with a smaller footprint, increased capacity, and larger interconnect scale that automate and simplify deployment and turn-up tasks. By supporting all services, including mobility, universal aggregation expands the network provider’s application space and competitiveness.
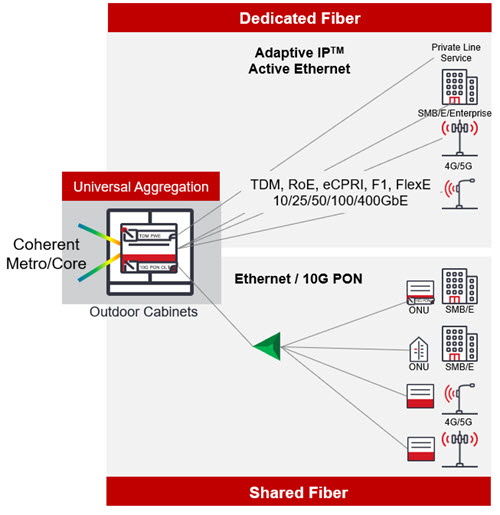
Universal Aggregation Solution
Increasingly, operators are looking to universal aggregation solutions to solve their business challenges with the right speeds, feeds, and routing capabilities to support traffic from multiple service types, including private line, business services, mobile, shared fiber, or Passive Optical Network (PON). Universal aggregation unifies packet and transport infrastructure. And best of all universal aggregation enables a simple, compact, scalable, and efficient programmable infrastructure with coherent optic transport, switching, and routing capabilities for 4G/5G services now and in the future.
The Challenges of Multi-Vendor, Multi-Layer Network Infrastructure
![]() For most network providers, their environment is a very challenging one with multiple vendors deployed for TDM, Ethernet, PON, and IP. It’s a no wonder performance and reliability is increasingly on their minds as they have to manually configure, shape, and optimize packet services while maintaining private line services. Most of these environments are capped investments making it difficult to support, as associated equipment and technical support becomes challenging.
For most network providers, their environment is a very challenging one with multiple vendors deployed for TDM, Ethernet, PON, and IP. It’s a no wonder performance and reliability is increasingly on their minds as they have to manually configure, shape, and optimize packet services while maintaining private line services. Most of these environments are capped investments making it difficult to support, as associated equipment and technical support becomes challenging.
![]() Another business challenge for network operators is having to deploy multiple platforms for different types of services. Having to manage multiple interconnected hardware and software deployments across complex environments increases operational cost, complexity, and troubleshooting tasks. Service margins will continue to erode, resulting in unsustainable financial pressures that negatively impact margins and the bottom line.
Another business challenge for network operators is having to deploy multiple platforms for different types of services. Having to manage multiple interconnected hardware and software deployments across complex environments increases operational cost, complexity, and troubleshooting tasks. Service margins will continue to erode, resulting in unsustainable financial pressures that negatively impact margins and the bottom line.
![]() Traditional TDM, Ethernet, PON, and IP network architectures are static, inflexible, and unable to scale quickly enough to support new high-bandwidth and low-latency services. To add capacity or deploy new revenue-generating services, like IoT or 5G, is difficult or impossible, as it requires network operators to deploy new or additional hardware and software and to build additional overlay networks to aggregate traffic from different types of services.
Traditional TDM, Ethernet, PON, and IP network architectures are static, inflexible, and unable to scale quickly enough to support new high-bandwidth and low-latency services. To add capacity or deploy new revenue-generating services, like IoT or 5G, is difficult or impossible, as it requires network operators to deploy new or additional hardware and software and to build additional overlay networks to aggregate traffic from different types of services.
![]() Building and operating standalone network architectures to support different types of services (ex. private line, business, mobile, residential, and shared fiber or PON services) creates a costly, complex, and inefficient network footprint that increases both CAPEX and OPEX. Multiple network architectures also mean increased management requirements and associated complexity, which reduces margins and negatively impacting the bottom line.
Building and operating standalone network architectures to support different types of services (ex. private line, business, mobile, residential, and shared fiber or PON services) creates a costly, complex, and inefficient network footprint that increases both CAPEX and OPEX. Multiple network architectures also mean increased management requirements and associated complexity, which reduces margins and negatively impacting the bottom line.
T![]() raditional network architectures are often unable to aggregate traffic from new types of services without additional hardware and software deployments in the network. This affects time-to-market for new service revenues and for existing customers reduced customer satisfaction. Risking current profitable revenue streams to another provider who can provide these and new services with velocity.
raditional network architectures are often unable to aggregate traffic from new types of services without additional hardware and software deployments in the network. This affects time-to-market for new service revenues and for existing customers reduced customer satisfaction. Risking current profitable revenue streams to another provider who can provide these and new services with velocity.
MNO Wholesale – Reseller Model
An MNO typically has extra capacity they sell at wholesale prices to resellers who in turn sell it to consumers, under their brand and at reduced retail prices. MNVOs can sell at lower prices because they only purchase the minutes wholesale and do not license radio spectrum or build and maintain the infrastructure. This give MNVOs more marketing dollars to market the product. MNO’s typically partner with MVNOs to get help with lost revenue from cancelled users from their network, competitive networks, and new users – boosting their bottom line. Mobile Virtual Network Enablers offer MNVOs network devices and equipment and BSS/OSS services.
Partnering with an MVNE is typically based on the size of the MVNO, their business models, and infrastructural capabilities. There are four types of MVNOs:
- Full MVNO
- Light MVNO
- Second Brand MVNO
- Branded Reseller MVNO
Full MVNO’s, as the name implies, are at the top or have the most capabilities in terms of resources, from network hardware, routing, service fulfilment and marketing and sales. Light MVNOs share resources with MNOs, have most of what Full MNVOs, but do not have networking infrastructure hardware. Two other MVNOs are Second Brand and Branded Reseller MVNOs. Second Brand MVNO’s, as the name implies, are a second brand for the partnering MVNO, have most of what Light MVNO’s have but use an MNO for application and service fulfilment. Branded Resellers use a MNO completely but have their own marketing and sales.
All can benefit from an MVNE, but smaller or skinny MVNOs benefit the most to reduce cost and enable a low entry point without major investments or infrastructure. Like MNO’s partnering with MVNOs, an MVNO typically partners with a Mobile Virtual Network Aggregator to increase revenue potential. MVNA’s can aggregate many smaller MVNOs into a single MVNO for MNOs. MNVAs reduce complexity while increasing their subscriber base by representing multiple bundled smaller MNVOs and providing access to MNOs allowing smaller MNVOs to focus on marketing costs.
Wholesale Benefits of Universal Aggregation
The value of universal aggregation is simple – choice! Choice from having to building different access networks for different mobile services. Choice from having different fiber for different services with unified fiber for different mobile services. Choice from aggregation for different services to aggregation for all services. Choice from closed Network Management Software (NMS) to open source streaming telemetry. Choice from having network revolutions to an evolution for all of your services, including 4G/5G.
A new simplicity for the Wholesale Operators
Ciena’s universal aggregation solution allows flexible, open deployments supported by our feature-rich extensive Packet Networking portfolio. Instead of building siloed, standalone architectures to support different types of services, wholesale operators can now bring more value to their networks by supporting concurrent PON, IP, and Ethernet services on the same Ciena aggregation platform. This improves customer satisfaction, choice, and business value control.
Stay tuned, as I discuss increased choice and control of business asset value for Cable MSO’s and Service Providers in the next two parts of Ciena’s universal aggregation series. To find out how to remove the constraints and bring more value to your network edge today, and ask us how Ciena helps Evolutionize Your Packet Network.
What’s in your Wholesale Network?









