The future of Ethernet services in the era of the Adaptive Network
Ethernet services have matured to become the indispensable backbone of our global network infrastructure. Now accounting for almost 80% of the global bandwidth connectivity services market and tens of billions in annual revenue, Carrier Ethernet continues to grow at a healthy pace – with port shipments increasing at double digit rates according to the latest figures from Vertical Systems Group.
But what lies ahead for the future of the business connectivity services market? The enterprise shift to cloud continues to shape their underlying network requirements, and new virtualizable services like SD-WAN continue to gain attention. Enterprises are increasingly asking for more flexibility, ease of use, and speed to market in the services they consume.
To address these needs, service providers continue the strides in their digital transformation journey, reflecting on initiatives in software automation, network efficiency, and operations agility. This transformational journey will have a significant impact on the services they can offer, their market reach, and the overall customer experience.
Let’s take a look as how Carrier Ethernet services will evolve as service providers pave their path towards digital transformation, and how the Adaptive Network can help Ethernet services evolve to provide an improved customer experience at optimized cost.
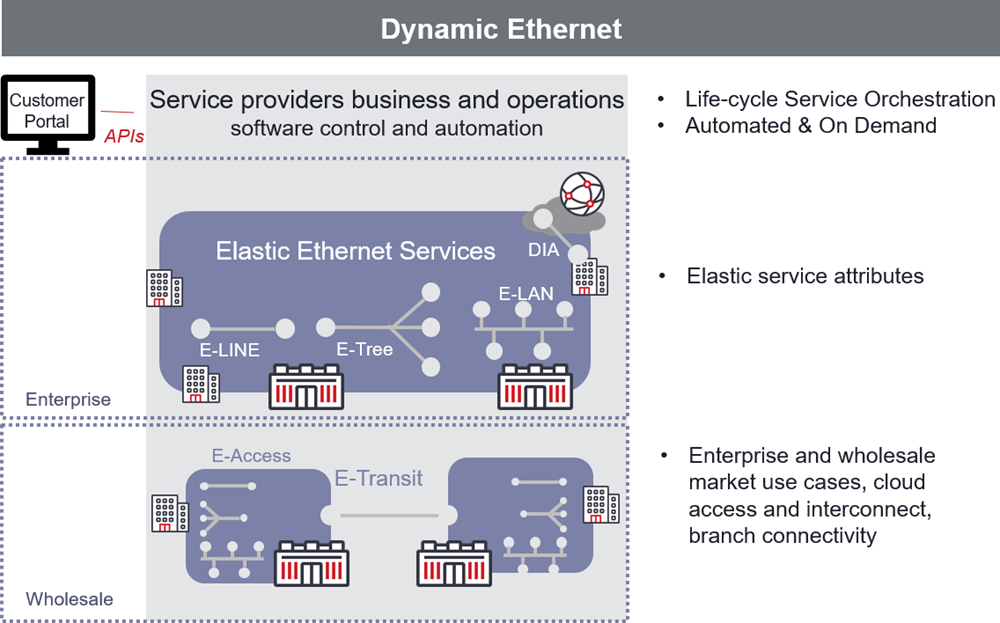
Dynamic Ethernet services
While Ethernet services bandwidth rates have shown a steady trend towards higher rates, the increasingly key requirement from customers of these services is elasticity in speed. Moving to evolve from fixed pre-defined connectivity service, Ethernet services can be requested through customer self-service portals, automated through services fulfillment workflows, provisioned over a programmable network that responds to software control and automation, and when the service needs to move/change/add/delete end-points the same dynamicity is available.
In this context, Dynamic Ethernet services are services with elasticity in bandwidth automated and orchestrated over the service lifecycle.
It is very well understood and accepted in the industry that ‘technically’ dynamic services allow network consumption similar to cloud resource consumptions. But the challenge remains on a viable business path. In reality, these connectivity services are carrying traffic from enterprise routers, switches, and IT environments that continue to demand fixed committed information rates (CIR). Additionally, the business end-users did not have the means to upgrade all the enterprise UNI ports.
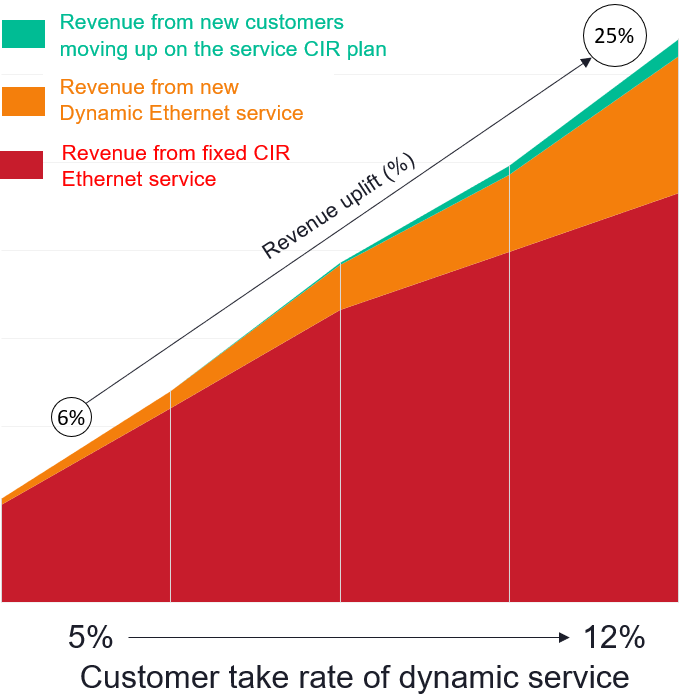
A viable and winning option for both end-customer and service provider is to start introducing higher rate Ethernet services on-demand, alongside the well-accepted fixed CIR services that enterprises and wholesale buyers of the Ethernet service are using. This approach will enable maintaining revenue from fixed CIR Ethernet services while also gracefully enabling enterprise and wholesale buyers to adopt on-demand and elastic Ethernet service attributes for certain business applications such as storage backup, or virtual machine migrations.
We looked at the revenue potential of hybrid service offers in case studies with service providers; for instance, offering metro and national Ethernet services with a fixed CIR but combined with elasticity to 10X higher speed that can be initiated on-demand. By and large, the case studies showed that with every percentage point increase in take rate of the 10X higher speed elastic on-demand service, there is potential for more than 2 percentage point uplift in revenue. Offering Dynamic Ethernet services can facilitate and smooth the transition to higher revenue for service providers.
In addition, the impact of these services includes improved time-to-revenue and cost savings. Automation case studies by and large promise about 70% savings in OpEx, and automated services have a faster time-to-market which will enable capturing customers faster resulting in improved revenue.
Intelligent Ethernet services emerging
From their initial conception until now, the essence of Carrier Ethernet services has been about measured and assured service performance. Established protocols like Y.1731 and TWAMP for service and network performance monitoring are now table stakes. As networks continue to disaggregate and operations continue to transform with more agility and automation, the challenge remains in how to deal with the growth of performance data collected via polling (e.g. SNMP) and telemetry (e.g. gRPC) methods. Furthermore, overlay of newer virtualizable services like SD-WAN in enterprise branch sites creates more need for truly understanding the overall enterprise connectivity requirements.
Performance metrics are captured in data records that represent a multitude of service performance indicators, including link utilizations, latency or congestion of virtual tunnels in the IP core, jitter and packet loss. Services assurance operations is challenged to deal with vast amounts of data, in a variety of forms and growing volume. Visualization, description, and diagnosis of the performance metrics data is essential for services assurance operational teams, as all these measures lead to ensure compliancy with customer’s SLA.
Intelligent Ethernet services use the powerful analytical platforms that can grasp the volume, variety, and velocity of services performance data, and combine it with artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to predict performance trends. Ethernet services are perhaps among the top business connectivity services that will benefit from analytics, AI/ML techniques as these connectivity services have to meet stringent performance for business applications. There is also an immediate cost benefit as most often service providers provide a credit payment back to the enterprise customers when there is violation in SLA metrics.
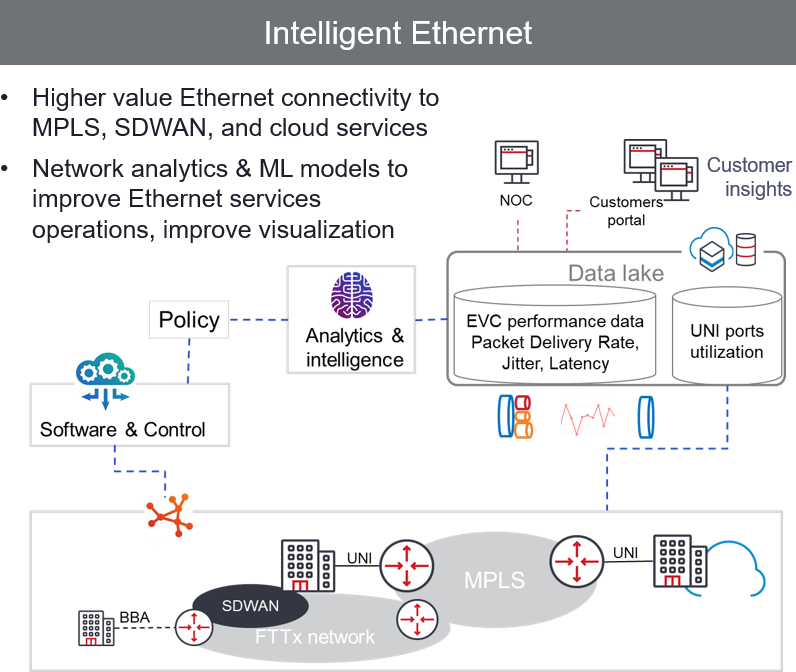
Analytics and intelligence that deliver improved service assurance can also enhance services revenue, as SLA portals are often priced as an add-on feature above the base connectivity or used as a differentiating feature to capture customers away from competitive offers.
Elastic EVPN slices
With the evolving adoption of cloud-based architectures, proliferation of connected devices and things, and insatiable demand for speed, network and cloud resources undergo constant evolution and change.
To meet the requirements for business applications performance, datacenters and cloud resources are distributing to come closer to the end-users. And like-wise there is a need to simplify and scale the networks at the same time. It is now well understood in the industry that dedicating network resources to one-off use cases is a highly inefficient model that results in high cost of infrastructure (hardware) and operations (software). Network slicing bears the promise to solve the situation of allocation of network resources to specific industrial use cases, coupled with software-defined and virtualized networking function platforms (SDN and NFV) to achieve the performance at optimized cost.
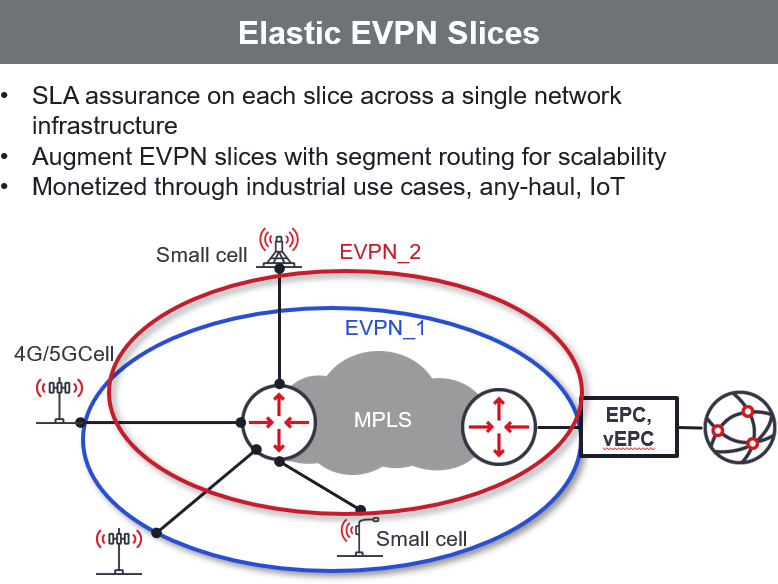
Ethernet Virtual Private Networks (EVPNs) are gaining traction as the fabric of network slicing due to their ability to deliver highly customizable, but private and secure, connectivity. EVPNs provide any-any connectivity in a secure and scalable fashion and are considered to be the evolution of L3 VPNs, but built with BGP scalability to implement both L2 and L3 VPNs.
In LTE and emerging 5G networks, there is fair amount of distribution of functionalities between cell sites and core in order to improve throughput and resolve hand-over and interference challenges. A rich and automated any-to-any connectivity is required to enable flow of data and control traffic seamlessly between cell sites and core. Using traditional IP methods is believed to be complex and lacks the scalability. Providers are considering more efficient and scalable solutions based on EVPNs.
Providers of Carrier Ethernet services have historically offered Ethernet Virtual Connections (EVC)s as a solution for mobile backhaul. These offers are now changing to Ethernet Service Slices as a group of Ethernet Services Virtual Connections (EVC), augmented with IP forwarding from Segment Routing. EVPN as a network slice is a new category of Ethernet Service offering that can be monetized for mobile wholesale offers to MNOs.
Cloud and mobility has had a profound impact on how people and machines connect, and this impact is ever-shifting and expanding. The key to success for managed service providers is the ability to adapt to this shift. As networks adapt, the services delivered over these networks must adapt as well. The path forward for Ethernet services in our era of the Adaptive Network bears great potential for improved revenue at optimized cost, and that is a good recipe for a successful services evolution.






