From hyperscaler growth to AI-powered networks, wave services are the unsung heroes enabling tomorrow’s connectivity. Explore what’s driving this transformation in a new report from Ciena.
 In an era defined by accelerated digital transformation, the demand for high-capacity, low-latency connectivity has never been greater. Ciena’s recently published Wave Services Report, offers a comprehensive look at how wave services—built on dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) technology—are evolving to meet the needs of a rapidly transforming global network landscape.
In an era defined by accelerated digital transformation, the demand for high-capacity, low-latency connectivity has never been greater. Ciena’s recently published Wave Services Report, offers a comprehensive look at how wave services—built on dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) technology—are evolving to meet the needs of a rapidly transforming global network landscape.
Let’s take a look at the high-level findings inside the Wave Services Report.
The backbone of the digital world
Wave services are the unsung heroes of modern connectivity. They form the foundation of wireline communications, enabling massive data transfers between data centers, cloud regions, and across continents via terrestrial and submarine networks. As cloud computing, AI, and edge technologies surge, wave services are becoming more intelligent, scalable, and essential.
From 2024 to 2031, international telecommunications capacity is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 26%, according to industry analysts at TeleGeography.
Hyperscalers—large-scale cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure—are leading this charge, with over 70 new data centers and 35 new cloud regions expected in 2025 alone.
Key market drivers
Three major forces are shaping the wave services market:
- Data center expansion: AI workloads are pushing data centers to the edge—closer to power sources and end users, people and machines. This decentralization demands robust interconnectivity, especially between training and inference data center locations.
- Cloud region growth: Cloud providers are shifting from large clusters to smaller, strategically placed regions to meet latency, compliance, and availability needs.
- Submarine and terrestrial network growth: With over 160,000 km of new submarine cables planned for 2025, global undersea connectivity is expanding rapidly.
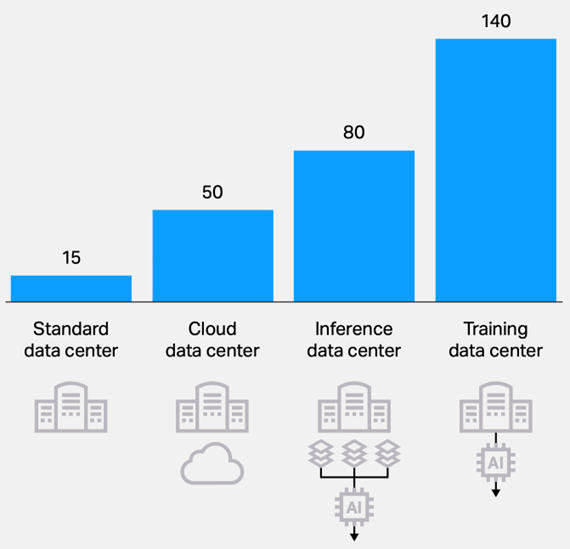
Figure 1: Typical KW per rack by service segment (Source - Ciena market analysis)
AI and the rise of specialized infrastructure
AI is truly a game-changer. Training and inference workloads require immense power and cooling, prompting the development of purpose-built AI data centers. These facilities are categorized into standard, cloud, inference, and training centers, each with unique connectivity needs.
Network as a Service (NaaS): A cloud-like experience
NaaS is evolving into a flexible, intelligent service model. Ciena outlines a three-phase roadmap:
- Phase 1: Pre-provisioned capacity with rapid service activation via APIs.
- Phase 2: Dynamic, pay-as-you-go services that scale with demand.
- Phase 3: Shared infrastructure across providers, enabling seamless, end-to-end services.
AI enhances NaaS by enabling predictive traffic management, energy-efficient routing, and self-optimizing networks.
Industry-specific opportunities
It should be noted that wave services are not one-size-fits-all, as different industries and markets have unique requirements, such as the finance and healthcare verticals.
- Finance: Demands ultra-low latency and high security for applications like algorithmic trading and fraud detection. The sector is rapidly adopting 400G wave services.
- Healthcare: Requires reliable, encrypted connections for telemedicine, diagnostics, and medical imaging. The shift to 400G is underway, supported by NaaS models for scalable upgrades.
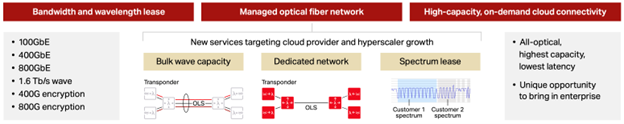
Hyperscalers and Managed Optical Fiber Networks (MOFN)
Hyperscalers are increasingly turning to managed services to meet their connectivity needs where Ciena identifies three emerging business models:
- Bulk wave capacity: Dedicated wavelength services using preferred technologies.
- MOFN dedicated network: End-to-end fiber networks managed by service providers.
- Hybrid Open Line Systems (OLS): Providers build the OLS, while hyperscalers deploy their own transponders.
Figure 2: Three new business models targeting hyperscalers
These models offer flexibility, scalability, and operational efficiency, allowing hyperscalers to focus on core business while leveraging service providers’ expertise.
Security, automation, and spectrum services
In today’s world, security is paramount. Wave services now offer Layer 1 encryption, including integration with quantum key distribution (QKD) systems for next-generation protection. Automation is also a key feature, with APIs enabling real-time service provisioning and performance monitoring.
The road ahead
As digital transformation accelerates unabated, wave services will continue to evolve with future developments focused on the following:
- Higher speeds (up to 1.6 Tb/s)
- Advanced encryption and QKD integration
- AI-driven automation and optimization
- Expanded NaaS offerings
- Deeper integration with cloud and edge ecosystems
Ciena’s report underscores the critical role of wave services in enabling the next generation of digital infrastructure. By embracing innovation and collaboration, service providers can meet the growing demands of hyperscalers, enterprises, and industries worldwide.
Want more detailed information? Then download the report today!