5 Benefits Layer 1 Encryption-as-a-Service Brings to Your Security Strategy
While most of the emphasis on protecting networks today is focused on protecting data within the enterprise or data center, the physical infrastructure of both public and private networks that connect these data centers are just as vulnerable to calculated attacks. A 2016 global security report by cyber security firm Trustwave reveals that the share of cyber incidents focused on corporate and internal networks has more than doubled, increasing from 18% in 2014 to 40% in 2015.
As increasingly more sensitive information gets distributed across fiber-optic networks, given all the efforts to lock down data at rest with firewalls, anti-virus software, and intrusion detection, cyber criminals are increasingly turning their attention to intercepting the data as it travels across the network.
A 2016 global security report by cyber security firm Trustwave reveals that the share of cyber incidents focused on corporate and internal networks has more than doubled, increasing from 18% in 2014 to 40% in 2015.
In terms of impact, a 2016 Ponemon study concluded that 52% of respondents’ companies had been victims of breaches within the last year - more targeted industries such as healthcare, finance, government, and education report breaches far exceeding the average.
Leveraging optical encryption as part of a holistic security strategy addresses all of these concerns and is the only way to secure everything on the communications link in and out of a facility rendering all data undecipherable to any hacker that taps into the fiber strand.
Easing the security burden with Encryption-as-a-Service
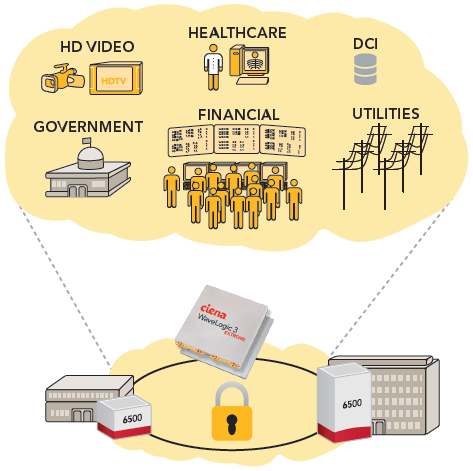
Service providers such as Lightower Fiber Networks, who recently announced their Encryption-as-a-Service (EaaS) offering using Ciena’s WaveLogic Encryption solution, are making it easier than ever for enterprises to cost-effectively leverage these benefits. For starters, a managed encryption service solution eliminates the burden and cost of having to purchase, deploy and manage the equipment as this is completely taken care of by the provider.
 Here are a few other reasons why organizations in today’s threat-based environments should strongly consider EaaS:
Here are a few other reasons why organizations in today’s threat-based environments should strongly consider EaaS:
Guaranteed 24/7 Data SecurityToday, EaaS offerings can provide a set-and-forget approach, where encryption is always on, no matter what. This ensures the highest level of security and eliminates human error that can result in sensitive information being sent over the network unencrypted (think private patient data or critical financial transactions).
Maximum Network PerformanceA layer 1 solution guarantees transparent encryption at wire-speed by eliminating encryption headers used at higher layers like Ethernet or Internet Protocol. This results in a fully protocol-agnostic platform to address a wide range of applications, where the encryption process does not reduce the traffic throughput of the signal being encrypted, nor does it modify the end-user data in any way.
Low Network Latency It’s no secret that in today’s day and age, latency can have a major impact on system performance and directly impact the user experience. Contrary to higher layer encryption solutions, state-of-the-art optical encryption meets the strictest latency requirements with latency measured in a few microseconds or less. For healthcare, network latency can mean the difference between life and death. For finance, network latency can directly affect the company profit. For utilities, network latency can mean the difference between containing or propagating a power outage across the grid.
‘Safe Harbor’ Exemption for Reporting a Breach
One major benefit of encrypting in-flight data is the potential exemption from regulatory requirements to report a data breach. Throughout the world, there is an increasing focus on the protection of customer data and quickly notifying those affected if their data is stolen. A common theme is the increasing size of penalties for breaches and for failing to notify that a breach has occurred within stipulated timescales. However, a commonly applied caveat is that if a data breach occurs but the data is unusable to the hacker, which is easily achieved with a Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 140-2 compliant encryption solution, the associated penalties may be waived. For healthcare providers as an example, where nearly 90% have been hit by data breaches in the last two years, the potential ‘safe harbor’ exemption from the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requirement to report a data breach is a key advantage.
Secure End-User ControlAnother important advantage of Layer 1 EaaS is the ability to partition encryption management from transport management. For EaaS, this capability ensures that the owner of the data maintains full control of the encryption security parameters associated with their critical data, and simplifies the process of issuing new keys or certificates as required by the company’s security policies.
For healthcare providers as an example, where nearly 90% have been hit by data breaches in the last two years, the potential ‘safe harbor’ exemption from the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requirement to report a data breach is a key advantage.
Encryption of data at rest and in flight is not mutually exclusive either. Both are typically implemented in conjunction and complement each other as part of a holistic security strategy. As increasingly more sensitive information gets distributed across fiber-optic networks, companies of all sizes must deploy an IT security approach that encompasses not just server security and at-rest data encryption, but also a robust in-flight data encryption solution to ensure data is protected from unauthorized discovery as it traverses the network. Ciena’s WaveLogic Encryption solution combines a high degree of flexibility and security, with ease of operation and administration, to enable a cost-effective, high-capacity, wire-speed encryption solution for secure collaboration between stakeholders.
With Ciena, this can be a reality for virtually all in-flight data, all the time.







