Igniting residential broadband for all takes more than funding alone
The global pandemic has shed light on a serious problem affecting communities around the world and their ability to achieve their full potential - the absence of affordable, fast, and reliable residential broadband services. While the digital divide has been discussed and debated by myself and many others for decades, the massive changes in how we live, work, and play has brought its consequences to the forefront.
The challenges related to ubiquitous broadband access are more than just a technical undertaking to be solved by a handful of engineers in R&D labs. The business case must also make sense, meaning we must address both technology and economic challenges if we’re to successfully solve the global challenge of ubiquitous and affordable broadband access to shape our communities and the world around us.
That’s why residential broadband networks are being addressed from multiple directions and stakeholders. In addition to communications service providers (CSPs) of all sizes, including Cable MSOs, we’re witnessing increased attention from utility providers, municipalities, and even federal governments.
All of these stakeholders realize that the scale of the challenge in front of us as an industry is great and diverse. But by strategically evolving broadband networks, we can realize a digital future for all by providing what has quickly become an essential human need.
More than just faster download speeds
Residential broadband network requirements have significantly evolved over the past few years. Today’s household is likely to have some members working or studying from home using cloud-based, real-time applications. Enjoying streaming events and movies and immersive online games are often the focal points of evening family entertainment. This makes low latency, symmetric bandwidth, high availability, and a great overall user experience just as important as the faster download speeds that seem to get all the headlines.
And, as we look ahead to how the Metaverse will impact personal interactions, entertainment, and business relationships, it’s quite clear that today's networks are ill-equipped for this expected evolution into a more virtual world.
Episode 56: Igniting a Digital Future for All with Improvements in Residential Broadband
Unprecedented government funding to bridge the digital divide
In my conversations with many across the industry, it’s clear that the greatest challenge to digital inclusion is viable economics. Even with an estimated $60 billion spent annually on building our global network infrastructure, implementing a network that provides broadband connectivity in low-density or low-income areas has always presented a very challenging business case.
But there’s good news on this front. To address the digital divide and digital inclusion, governments worldwide have announced hundreds of billions of dollars in stimulus programs to support network operators deploying networks in remote and rural areas. They also have programs to subsidize broadband access in low-income areas, creating a more appealing business environment. Network operators themselves have also announced massive private broadband investments to address the residential broadband situation.
Although stimulus funding and private operator investments help the business case for residential broadband modernization and expansion, it does not provide a complete answer. Budgets have limits, and the cost of deploying and operating the network well into the future, as well as the cost of constant technology refresh cycles, means that a positive business case has often proved unachievable. This is where those engineers in our R&D labs enter the picture…
New residential broadband network architecture for a more connected future
Another significant roadblock to widespread residential broadband solutions has been the splintered nature of the technologies that address it. This may now finally be changing through the combination of new global standards for high-speed broadband access and the continuous innovation that makes building and maintaining these networks more affordable for all.
Fiber-optics are the lifeblood of high-speed networks, and fiber-based Passive Optical Network (PON) has become the go-to access technology to implement the “last mile” of next-generation broadband networks. But limitations to previous generations like EPON and GPON, as well as the high cost and closed architectures of the equipment needed to support them, limited the value that PON could bring.
Fiber-optics are the lifeblood of high-speed networks, and fiber-based Passive Optical Network (PON) has become the go-to access technology to implement the “last mile” of next-generation broadband networks.
This created challenges for network operators. It forced them to compromise when building or evolving their residential broadband networks, challenging them in closing the digital divide, supporting the next generation of end-user applications, or improving affordability to their customer base.
What does this mean exactly? Limitations of legacy residential technologies force service providers to choose between overbuilding versus scalability, optimizing initial CAPEX versus futureproofing, improving customer quality of experience versus controlling OPEX, focusing on broadband only versus multiple services, and single vendor versus multi-vendor best-of-breed designs. None of these trade-offs should be part of the network operators' decision-making process. Igniting a digital future for all is far too important to compromise by adhering to outdated technologies and assumptions.
New Residential Broadband architectures can ignite a digital future for all
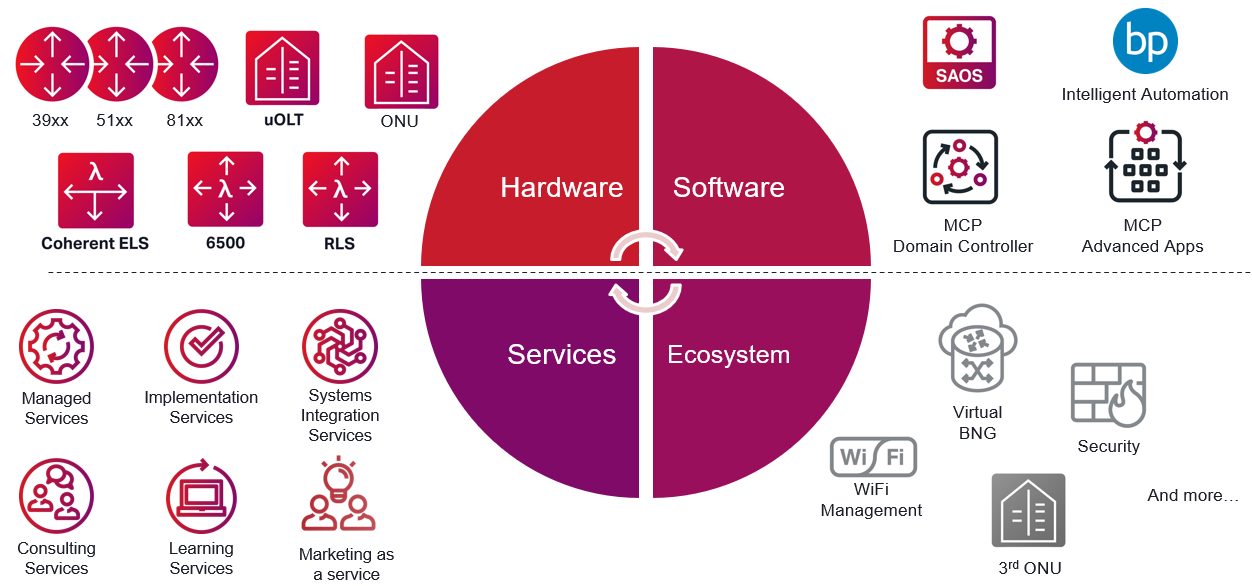
Service providers shouldn’t have to compromise on their residential broadband networks. But the same vendors and the same technology have been in use for years. Breaching the digital divide, reaching sustainability goals, and creating truly innovative services will require a new perspective. At Ciena, we believe Residential Broadband networks can be re-imagined around three key concepts:
Openness and Automation: Standards-based with open APIs facilitate building best-in-breed designs by leveraging the latest networking technology innovations. And using next-generation software automation and control can provide advanced analytics and visibility across network layers. This ensures that you can intelligently automate key operations and processes so you’re always ready to meet expected changes in demand.
Modularity: Start small and expand your network where and when required to operate more efficiently and protect your bottom line by leveraging technology that is truly power and space efficient along with the highest port density. This ensures you are deploying the most cost-optimized and sustainable solution.
Scalability: Build a high-capacity residential broadband network that easily and rapidly scales so you can deliver on your customer's expectations while protecting existing, and capturing new, revenue streams. Be sure that the solutions you deploy allow your network to scale dynamically and far beyond the current options in the market, as bandwidth demand obviously isn’t slowing.
Economic and environmental sustainability
Sustainability should be carefully considered when reviewing a next-generation residential broadband architecture. Here are Ciena, we understand that sustainability is often at the forefront of conversations with all constituents -- customers, investors, and employees.
So we continue to invest in the sustainability of all critical network elements by converging the access infrastructure with best-in-class routers, WaveLogic coherent optics, and innovative micro Optical Line Terminals (uOLTs) and corresponding Optical Network Units (ONUs).
Sustainability models show we have already helped our customers avoid more than 550,000 metric tons of CO2e over an eight-year period (2014–2021) with our Routing and Switching Platforms, which helped our customers’ production networks achieve 23 percent savings in power consumption. This equals 96,000,000 kWh saved resulting in $12 million per year OPEX savings.
Through our WaveLogic coherent optics investments, we introduced the industry’s first 400 Gb/s transceiver in 2017 and are delivering the pluggable version five years later at one-fifth the power, one-tenth the space, and with improved industry-leading systems performance.
Combining Ciena’s routing, optical, and PON innovations together offers significant improvements in footprint and power savings to enable more efficient and sustainable networks for our customers—and the planet at large. For example, evolving from a traditional pure PON chassis-based, multi-boxed solution to Ciena’s converged access with XGS-PON and routing in a single platform result in a 67 percent reduction in footprint and 63 percent reduction in power consumption.
Ubiquitous and affordable residential broadband for all
As the world recognizes the importance of digital inclusion to society’s progression, we must embark on a multi-faceted effort across our industry, as well as sustained support from governments and communities around the world. Ciena’s Residential Broadband Solution plays an important role, leveraging the latest in open, modular, and scalable technologies to help network operators build a sustainable residential network, so you don’t have to compromise.






