What is DCI?
Data Center Interconnect (DCI) technology connects two or more data centers together over short, medium, or long distances using high-speed packet-optical connectivity.
Data Centers house compute and storage resources for applications, data, and content. And in this cloud-based, application-centric world, access to that data is a critical challenge.
Data Centers need to talk to each other—to share data and content and provide back-ups for redundancy. Fortunately, DCI technology enables the transit of critical assets over any distance, from across town to ultra-long trans-Pacific or trans-Atlantic oceanic links and everything in-between. Data may be carried across simple, point-to-point connections, more robust ROADM-based networks, or open line systems which support transport interfaces sourced from multiple vendors.
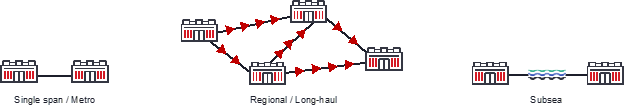
Distance requirements for DCI applications vary from metro to subsea
The most effective transport technology for DCI is next-generation coherent optics providing blazing speeds up to 800 Gb/s per wavelength. With a fast, reliable connection in place, physically separate data centers can easily share resources and balance workloads.
Some large operations use DCI to connect their own data centers within their extended enterprise infrastructures, while others connect to partners, cloud providers or data center operators to simplify data and resource sharing or handle disaster recovery needs. Subsea cables are used to connect data centers and internet exchanges between countries and continents separated by vast oceans.
Some DCI applications need the highest level of capacity and scalability along with more software control and automation, while others can trade off some performance to meet a specific power profile and form-factor.
Performance optimized DCI solutions are needed to overcome scalability and distance constraints to deliver higher capacity connectivity.

Increasing capacity and distance are key challenges for DCI networks
- Distance: DCI applications can vary greatly in size and scope. Data centers may be dispersed across a metro area, around a country, or all over the globe. Having enough performance to interconnect them while carrying the most bits the farthest is critical. Performance optimized coherent technology can transport more capacity at any distance, offering programmable interfaces with selectable baud and different modulation schemes to fine tune capacity for any application. In addition, for ROADM-based networks that provide greater flexibility and resiliency, performance optimized solutions offer the capability to transit multiple ROADM nodes across short metro links, as well as long-haul haul routes between major cities.
- Capacity: Data centers store and deliver the data that applications require. Data sets coming into or leaving a data center can be very large—from hundreds of Gigabits to Terabits. Routers are moving from 100GbE to higher speed 400GbE services. To handle these growing bandwidth demands, networking equipment must provide reliable, high-capacity connections that scale simply and quickly. Coherent optics, like Ciena’s WaveLogicTM 5, pave the way for data to move at rates up to 800 Gb/s on a single wavelength, increasing DCI capacity to a new industry benchmark. Furthermore, modern photonic line systems offer the ability to expand the usable spectrum from the C-band to include the L -band for double the capacity per fiber, allowing more wavelengths between data centers in fiber constrained or high growth areas.
Footprint optimized DCI solutions shrink the size of the coherent Digital Signal Processor (DSP) and electro-optics to fit within a standards-based pluggable form-factor. These pluggable interfaces provide IP/Optical integration without reducing faceplate density or stranding packet switching capacity. Footprint optimized solutions are attractive for access, edge, and metro DCI applications where spectral efficiency is less of a concern and service density, reduced power consumption, and smallest footprint are critical.
In addition to distance and capacity concerns, DCI networks face challenges associated with data security, simplifying operations, and reducing the cost per bit for connectivity.
Additional requirements commonly seen for DCI networks
- Security: Sensitive information is often stored in data centers. Financial transactions, personnel records, and other corporate data are all crucial and often highly confidential. As a result, DCI must be reliable, safe, and even encrypted to avoid costly breaches and data losses. Encryption and stringent rules for access to stored data are widely deployed to protect against intrusions, and advances in packet-optical networking equipment can deliver wire-speed, in-flight encryption to protect data as it travels over an optical DCI link.
- Operations: Minimizing the labor, complexity, slowness, and errors that arise from manual operations for commissioning, provisioning, and managing the DCI network is an operational imperative. Turning up a connection between two data centers must be simple and fast, and managing each connection should not require ongoing manual tasks. Standards-based open APIs and modern data models are critical to the shift to automation because they enable platform integration, scripting, and new ways to monitor and manage the network. Optical networking platforms designed and purpose-built for DCI applications can be managed through open interfaces or full lifecycle management software platforms, giving network operators the flexibility to manage the DCI network the way that they want.
- Cost: Large data streams entering and leaving data centers must be carried as cost-efficiently as possible, so lowering the cost per bit for interconnect is an ongoing concern. To reduce interconnect cost/bit while offering more capacity scalability, the industry is making advances in high-speed coherent interfaces to increase capacity per wavelength and improve performance to drive those bits longer distances. Additionally, compact, modular interconnect devices, such as Ciena’s Waveserver® family of products, are designed to minimize footprint and power requirements and reduce ongoing operational costs across the lifetime of the DCI system.
DCI technology sits at the center of the cloud-centric world, providing the network capacity for users and applications to connect to storage, compute, and content resources.
Ciena offers best-in-class coherent optics with performance optimized and footprint optimized solutions to fit any DCI application space, packaged in a way that is simple to use, scalable, and tailored to each network’s needs.




