5 Most Important Fiber Deep Acronyms
Acronyms are a huge part of language, some are universal, while others unique and indecipherable, making sense only to those in the know. But once you figure what these indecipherable acronyms really mean, a whole new world is unveiled – oh yeah, and typing becomes a whole lot easier too!
Every industry has its own set of unique acronyms, and the cable network is no exception, as they continue to modernize their networks. Fiber Deep is the architectural vision whereby cable operators push the packet-based optical-to-electrical conversion closer to the end-user – yielding a better customer experience through better service.
In this article I will explain, the top five Fiber Deep acronyms you’ll likely encounter. Even better, at the bottom of the article, you can download the complete Fiber Deep Glossary of Terms, explaining in simple terms over a hundred Fiber Deep acronyms and terms - bonus!
Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC)
Cable operators have used HFC outside plants for over two decades, delivering content and broadband services. HFC combines both optical fiber and electrical coaxial cable to deliver services to end-users. Fiber is used to carry upstream and downstream signals to/from the headend to a digital fiber node, where those signals are converted to Radio Frequency (RF) for distribution on a shared hardline coaxial cable and tapped using a smaller drop cable to customers.
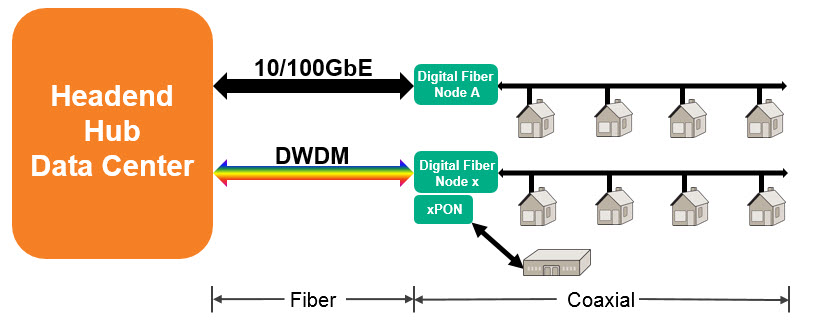
“Combines fiber and coax as a broadcast network to deliver cable operator services”
Converged Cable Access Platform (CCAP)
Prior to CCAP, some cable operators used different and separate analog systems to deliver linear video and cable modem functionality by using different Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) and Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS). Driven by huge demands in linear video, Video-on-Demand (VoD) and high-speed data, CableLabs, a not-for-profit innovation and research and development lab founded in 1988 by American cable operators, led the effort to combine two competing platforms from Comcast and Time Warner Cable, now known as CCAP.
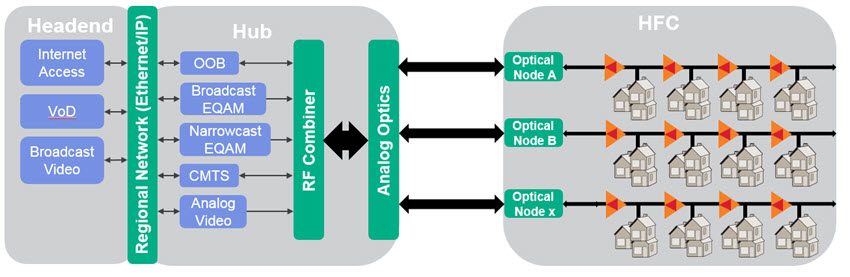
“CCAP is CableLabs’ effort combining QAM and CMTS functions, as well as enabling Internet Protocol (IP) video. Centralizing equipment in the headend or primary hub is commonly known as Centralized Access Architecture (CAA).”
Distributed Access Architecture (DAA)
With some cable operator’s networks seeing bandwidth doubling every 18 to 24 months, cable operators are strategically extending fiber to digital fiber nodes in a Distributed Access Architecture (DAA).
Two popular DAA approaches are Remote-PHY (P-PHY) and Remote-Media Access Control/PHY (R-MAC/PHY). R-PHY moves digital signal generation from the headend to the fiber node, making the headend to fiber node digital, enabling much better performance and higher bandwidth. R-MAC/PHY, along with digital signal generation, moves media processing to the fiber node, enabling even more space in the headend/hub locations. 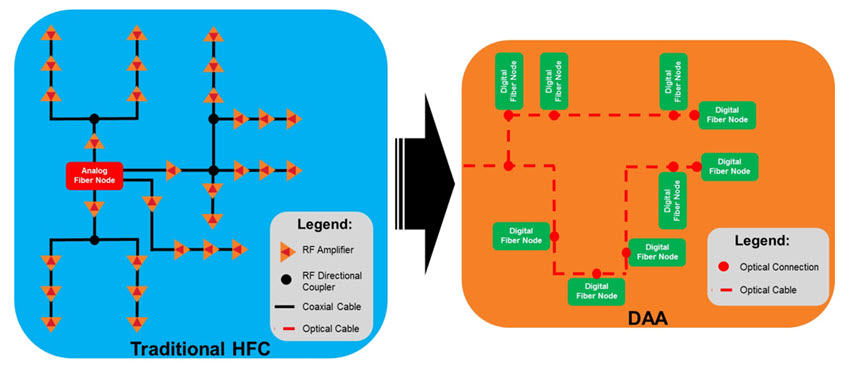
”DAA distributes MAC and PHY layer functions of CMTS, EQAM, or CCAP to a node, cabinet or Multi Dwelling Unit (MDU) location.”
Data Over Cable Services Interface Specification (DOCSIS)
DOCSIS is the international standard developed by CableLabs used to provide Internet access over the cable system. Over the years, as bandwidth demand grew, DOCSIS answered the call by enabling fiber-like Gigabit per second capacity.
DOCSIS has become one of the key elements helping cable operators dominate broadband services.
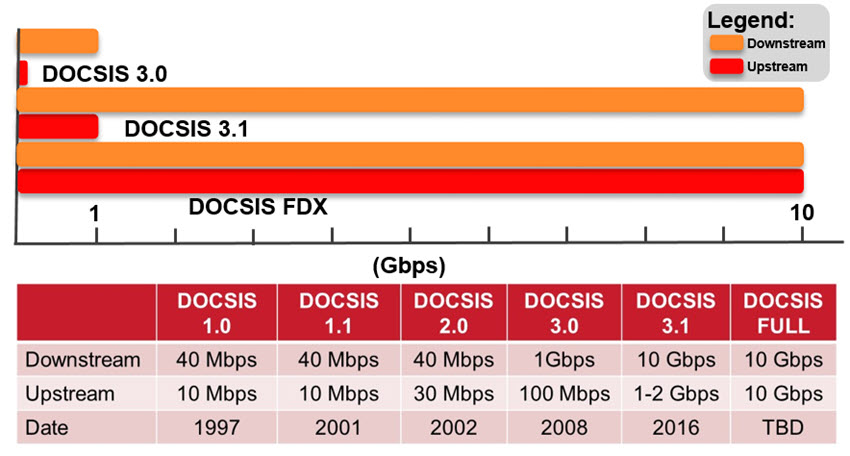
“CableLabs specification used to provide Internet service using a cable modem.”
Remote PHY Device (RPD)
RPD is the actual device that provides the R-PHY or R-MAC/PHY function inside a remote/fiber node. This allows the CCAP function to be separated into two components, the CCAP core and the RPD. While the CCAP core function remains in the headend/hub, the RPD can be distributed to a digital fiber node, cabinet or MDU location.
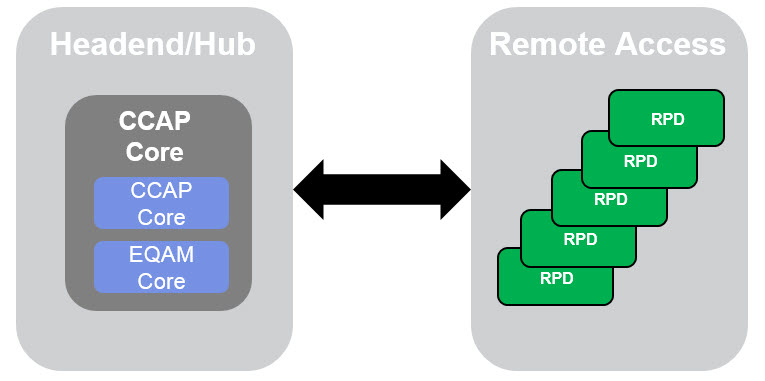
“Remote device providing the DOCSIS R-PHY function”
As the cable industry evolves, so will its language, so stay on top by downloading the Fiber Deep Glossary of Terms, a simple easy to read guide to help “be in the know”.
Ciena’s Fiber Deep Solution lights the way for cable access modernization with our industry-leading Waveserver Ai, Coherent Packet Networking 8180, and 6500 Reconfigurable Line System (RLS) system that together offer a high-performance yet cost-effective coherent optical transport solution with integrated packet switching capabilities. DFN aggregation is addressed using our award winning 5170 Service Aggregation Switch.
So, are you ready for Fiber Deep?
Ask us how Ciena helps build the next generation fiber distribution network.
Want to learn more? Watch Ciena’s Chalk Talk: Fiber Deep on how cable operators are putting high capacity anywhere in their network by pushing fiber deeper.







